 中俄宣布合建月球基地,大洋对岸的人急了!
中俄宣布合建月球基地,大洋对岸的人急了!
China signs deal with Russia to build a power plant on the moon — potentially leaving the US in the dust
译文简介
美国人现在的心态是:我不行,我也不准你行
正文翻译
China signs deal with Russia to build a power plant on the moon — potentially leaving the US in the dust
Story by Ben Turner · 7h
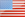
中国月球基地设想图。中国宣布与俄罗斯合作,计划于2036年前建成月球核电站。

An illustration of a hypothetical Chinese moon base. China has announced a deal with Russia to build a lunar power plant by 2036.
中国月球基地设想图。中国宣布与俄罗斯达成协议,将在2036年前在月球上建造一座(核能)发电厂。
Russia has signed a deal with China to build a nuclear power plant on the moon.
The Russian reactor will be used to power the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS), jointly led by China and Russia, and should be completed by 2036, according to a memorandum of cooperation signed by the two nations.
The announcement comes just after NASA revealed a 2026 budget proposal that would axe the agency's plans for an orbital lunar base.
中国月球基地设想图。中国宣布与俄罗斯合作,计划于2036年前建成月球核电站。
俄罗斯已与中国签署协议,将在月球建设核电站。
根据两国签署的合作备忘录,该核反应堆将为中俄共同主导的"国际月球科研站"(ILRS)供电,预计于2036年竣工。此项声明发布之际,NASA刚公布2026年预算提案,拟取消其轨道月球基地计划。
The construction of the Chinese-Russian reactor will likely be carried out autonomously "without the presence of humans," according to a 2024 interview with Yury Borisov, director general of the Russian space agency Roscosmos, on the Russian state-owned news site TASS. While details of how this can be achieved remain unclear, Borisov added that the technological steps are "almost ready."
"The station will conduct fundamental space research and test technology for long-term uncrewed operations of the ILRS, with the prospect of a human being's presence on the Moon," Roscosmos wrote in a May 8 announcement following the signing of the memorandum.
俄罗斯国有新闻网站塔斯社(TASS)在2024年对俄罗斯航天局(Roscosmos)局长尤里·鲍里索夫(Yury Borisov)的采访中表示,中俄反应堆的建设可能会在“无人”的情况下自主进行。虽然如何实现这一目标的细节尚不清楚,但鲍里索夫表示相关技术"已基本就绪"。
俄航天集团在5月8日签署备忘录后的公告中写道:"该站将开展基础空间研究,测试国际月球科研站(ILRS)长期无人运行技术,并为未来载人登月奠定基础。"
The new research station, a permanent, manned lunar base located on the moon's south pole, has so far attracted 17 countries to join the program — including Egypt, Pakistan, Venezuela, Thailand and South Africa. Its groundwork will be laid by China's 2028 Chang'e-8 mission, which will be the nation's first time landing an astronaut on the lunar surface.
The roadmap for the ILRS was first unveiled in June 2021, with China and Russia announcing they would loft the pieces for a robotic moon base using five super heavy-lift rocket launches from 2030 to 2035.
这座位于月球南极的永久性载人科研基地,目前已吸引17国加入计划,包括埃及、巴基斯坦、委内瑞拉、泰国和南非。中国2028年的嫦娥八号任务将为其奠定基础,这也将是中国首次实现航天员登月。
ILRS路线图最早于2021年6月公布,中俄计划在2030至2035年间通过五次超重型火箭发射,将机器人月球基地组件送入太空。
Once these basic pieces are established, China plans additional launches that will extend the base further, connecting it to a space station orbiting the moon and two nodes located at the moon's equator and its far side, Wu Yanhua, the chief designer of China's deep exploration project, said at a 2024 media conference, according to state media outlet xinhua.
This extended model, laying the foundations for manned landings on Mars, should be completed by 2050. It "will be powered by solar, radioisotope and nuclear generators," Wu said. "It will also include lunar-Earth and high-speed lunar surface communication networks, as well as lunar vehicles like a hopper, an unmanned long-range vehicle, and pressurized and unpressurized manned rovers."
中国深空探测工程总设计师吴艳华在2024年一场媒体发布会上表示,待这些基础模块建成后,中国计划通过后续发射任务进一步扩展基地规模。据官方媒体新华社报道,扩建计划包括将月面基地与环月轨道空间站相连,并在月球赤道区域和背面增设两个枢纽节点。
这种扩展模式将为载人登陆火星铺路,预计2050年完成。吴艳华指出:"该系统将由太阳能、同位素和核能发电机供电,包含月地通信网络、高速月表通信网络,以及跳跃器、无人长距漫游车、加压与非加压载人月球车等设备。
The memorandum comes at a time of growing ambition for China's space programs. The country has had a lunar presence since the 2013 landing of the Chang'e 3 mission, which placed a rover on the moon. Subsequent missions landed more rovers on the moon and Mars, while collecting samples from the moon's near and far sides, and mapped out the lunar surface.
China's race to build a lunar outpost also has an American rival in the Artemis program, which has recently been beset by delays. Artemis III, which will see NASA astronauts return to our nearest natural satellite for the first time in over 50 years, is expected to launch sometime in 2027.
这份备忘录的签署,展现出中国航天前所未有的雄心壮志。自 2013 年嫦娥三号任务成功着陆月球并部署月球车以来,中国就一直保持着在月球上的活动。随后的一系列任务让更多的月球车登陆月球和火星,同时从月球近月面和远月面采集样本,并绘制了月表地图。
中国致力于建造月球前哨站,而美国的 “阿尔忒弥斯” 计划是其竞争对手。该计划最近一直受到各种延误的困扰。“阿尔忒弥斯三号” 任务预计将让美国国家航空航天局(NASA)的宇航员在时隔 50 多年后首次重返距离我们最近的这颗天然卫星,它预计将于 2027 年的某个时候发射。
Meanwhile, the future of NASA's own planned lunar space station, dubbed Gateway and initially slated for launch as soon as 2027, has been thrown into question with the release of the Trump administration's proposed 2026 budget. The budget calls for canceling the Gateway mission, despite significant progress on building the station's modules.
与此同时,美国国家航空航天局(NASA)自己计划建造的名为 “门户” 的月球空间站,原本最早定于 2027 年发射,随着特朗普政府公布的 2026 年预算提案的出台,其未来也受到了质疑。该预算案要求取消 “门户” 任务,尽管在建造空间站舱段方面已经取得了重大进展。
Story by Ben Turner · 7h
中国月球基地设想图。中国宣布与俄罗斯合作,计划于2036年前建成月球核电站。

An illustration of a hypothetical Chinese moon base. China has announced a deal with Russia to build a lunar power plant by 2036.
中国月球基地设想图。中国宣布与俄罗斯达成协议,将在2036年前在月球上建造一座(核能)发电厂。
Russia has signed a deal with China to build a nuclear power plant on the moon.
The Russian reactor will be used to power the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS), jointly led by China and Russia, and should be completed by 2036, according to a memorandum of cooperation signed by the two nations.
The announcement comes just after NASA revealed a 2026 budget proposal that would axe the agency's plans for an orbital lunar base.
中国月球基地设想图。中国宣布与俄罗斯合作,计划于2036年前建成月球核电站。
俄罗斯已与中国签署协议,将在月球建设核电站。
根据两国签署的合作备忘录,该核反应堆将为中俄共同主导的"国际月球科研站"(ILRS)供电,预计于2036年竣工。此项声明发布之际,NASA刚公布2026年预算提案,拟取消其轨道月球基地计划。
The construction of the Chinese-Russian reactor will likely be carried out autonomously "without the presence of humans," according to a 2024 interview with Yury Borisov, director general of the Russian space agency Roscosmos, on the Russian state-owned news site TASS. While details of how this can be achieved remain unclear, Borisov added that the technological steps are "almost ready."
"The station will conduct fundamental space research and test technology for long-term uncrewed operations of the ILRS, with the prospect of a human being's presence on the Moon," Roscosmos wrote in a May 8 announcement following the signing of the memorandum.
俄罗斯国有新闻网站塔斯社(TASS)在2024年对俄罗斯航天局(Roscosmos)局长尤里·鲍里索夫(Yury Borisov)的采访中表示,中俄反应堆的建设可能会在“无人”的情况下自主进行。虽然如何实现这一目标的细节尚不清楚,但鲍里索夫表示相关技术"已基本就绪"。
俄航天集团在5月8日签署备忘录后的公告中写道:"该站将开展基础空间研究,测试国际月球科研站(ILRS)长期无人运行技术,并为未来载人登月奠定基础。"
The new research station, a permanent, manned lunar base located on the moon's south pole, has so far attracted 17 countries to join the program — including Egypt, Pakistan, Venezuela, Thailand and South Africa. Its groundwork will be laid by China's 2028 Chang'e-8 mission, which will be the nation's first time landing an astronaut on the lunar surface.
The roadmap for the ILRS was first unveiled in June 2021, with China and Russia announcing they would loft the pieces for a robotic moon base using five super heavy-lift rocket launches from 2030 to 2035.
这座位于月球南极的永久性载人科研基地,目前已吸引17国加入计划,包括埃及、巴基斯坦、委内瑞拉、泰国和南非。中国2028年的嫦娥八号任务将为其奠定基础,这也将是中国首次实现航天员登月。
ILRS路线图最早于2021年6月公布,中俄计划在2030至2035年间通过五次超重型火箭发射,将机器人月球基地组件送入太空。
Once these basic pieces are established, China plans additional launches that will extend the base further, connecting it to a space station orbiting the moon and two nodes located at the moon's equator and its far side, Wu Yanhua, the chief designer of China's deep exploration project, said at a 2024 media conference, according to state media outlet xinhua.
This extended model, laying the foundations for manned landings on Mars, should be completed by 2050. It "will be powered by solar, radioisotope and nuclear generators," Wu said. "It will also include lunar-Earth and high-speed lunar surface communication networks, as well as lunar vehicles like a hopper, an unmanned long-range vehicle, and pressurized and unpressurized manned rovers."
中国深空探测工程总设计师吴艳华在2024年一场媒体发布会上表示,待这些基础模块建成后,中国计划通过后续发射任务进一步扩展基地规模。据官方媒体新华社报道,扩建计划包括将月面基地与环月轨道空间站相连,并在月球赤道区域和背面增设两个枢纽节点。
这种扩展模式将为载人登陆火星铺路,预计2050年完成。吴艳华指出:"该系统将由太阳能、同位素和核能发电机供电,包含月地通信网络、高速月表通信网络,以及跳跃器、无人长距漫游车、加压与非加压载人月球车等设备。
The memorandum comes at a time of growing ambition for China's space programs. The country has had a lunar presence since the 2013 landing of the Chang'e 3 mission, which placed a rover on the moon. Subsequent missions landed more rovers on the moon and Mars, while collecting samples from the moon's near and far sides, and mapped out the lunar surface.
China's race to build a lunar outpost also has an American rival in the Artemis program, which has recently been beset by delays. Artemis III, which will see NASA astronauts return to our nearest natural satellite for the first time in over 50 years, is expected to launch sometime in 2027.
这份备忘录的签署,展现出中国航天前所未有的雄心壮志。自 2013 年嫦娥三号任务成功着陆月球并部署月球车以来,中国就一直保持着在月球上的活动。随后的一系列任务让更多的月球车登陆月球和火星,同时从月球近月面和远月面采集样本,并绘制了月表地图。
中国致力于建造月球前哨站,而美国的 “阿尔忒弥斯” 计划是其竞争对手。该计划最近一直受到各种延误的困扰。“阿尔忒弥斯三号” 任务预计将让美国国家航空航天局(NASA)的宇航员在时隔 50 多年后首次重返距离我们最近的这颗天然卫星,它预计将于 2027 年的某个时候发射。
Meanwhile, the future of NASA's own planned lunar space station, dubbed Gateway and initially slated for launch as soon as 2027, has been thrown into question with the release of the Trump administration's proposed 2026 budget. The budget calls for canceling the Gateway mission, despite significant progress on building the station's modules.
与此同时,美国国家航空航天局(NASA)自己计划建造的名为 “门户” 的月球空间站,原本最早定于 2027 年发射,随着特朗普政府公布的 2026 年预算提案的出台,其未来也受到了质疑。该预算案要求取消 “门户” 任务,尽管在建造空间站舱段方面已经取得了重大进展。
评论翻译
很赞 ( 31 )
收藏
The moon has no atmosphere, and so Asteroids, meteors that are usually burned up in Earths Atmosphere, will hit the moon at 1000's of miles per hour.
They are just gonna play the odds?
月球没有大气层,所以那些在地球大气层中通常会被烧毁的小行星和流星,会以每小时数千英里的速度直接砸向月球。难道他们是想碰运气吗?
Hayden Nunes
dig in go subsurface, then the structures can be more robust...built in rock
往地下挖,深入地底啊,这样建筑物就能更坚固…… 建在岩石里。
Jerrold Carlile
"China signs deal with Russia to build a power plant on the moon" ... They won't have to build a very large power grid locally but if the power is to supply China they will need a long extension cord!
“中国与俄罗斯签署协议在月球上建造一座发电厂”…… 没必要在那里造一个庞大电网啊,如果电力是供给中国用的,那他们需要一根很长的电线即可!
Brian Huff
hat's what the whole world should be doing finding better solution's . Building a base on the moon is a big start . But this country and those counties can never get along to bad too. from the moon to Mar's and beyond If only we could work together to preserve Human kind instead of destroying it.
这就是全世界都应该做的事,探寻更好的解决方案。在月球上建造基地是一个重大开端。但这个国家(美国)和那些国家永远都无法和睦相处,这太糟糕了。从月球到火星以及更远的地方,如果我们能够共同努力保护人类,而不是毁灭人类就好了。
M*******
they mess up on the moon--it's over for earth
如果他们在月球上搞砸了 —— 那地球也就完蛋了
JJones
Huh? Solutions to what? Poverty? Hunger? The leftists are hell bent on destroying earth shutting down power plants of any kind including nuclear.
哈?解决什么的方案?贫困?饥饿?左派一心想要毁灭地球,关闭包括核电站在内的各种发电厂。
Dirk Michael
lets see if we can ruin another floating ball
让我们看看人类是否能毁掉另一个星球。
Ahmythian Draugh
yeah, we could all complain as much as we want but it doesn't mean anything when the fact is, China and Russia plan to do it lol American's are so quick to say "we don't need this and that" while our adversaries are doing exactly that and no ones telling them no because they can't. So, what can you do? Sit idly by while they accomplish it, or kick ourselves in gear and do it first? Reality is, we dont have enough support to even accomplish this in America.. The US used to be the home of technological breakthroughs.. Now its the home to feelings and the only breakthrough we're reaching is who identifies as who
确实,我们可以抱怨个没完,但事实摆在眼前——中俄就是铁了心要干这事(笑)。美国人总爱说"我们不需要这个那个",可对手却在闷声推进,没人能阻止他们,因为根本阻止不了。那能怎么办?眼睁睁看着他们成功,还是咬紧牙关抢先一步?现实是,美国现在连达成这种计划的支持度都凑不齐……这里曾是技术突破的摇篮,如今却成了情感政治的秀场,我们唯一的"突破"大概只剩性别认同辩论了。
JJones
Earths been around longer then nuclear power plants.
地球存在的时间比核电站要长得多。
Mikey M
Earth the day after nuclear Armageddon will be more hospitable to life than Mars today. And that's without including the radiation exposure seen when traveling from the Earth to/from Mars.
There is no Plan B: this Earth is all we have.
在核战争后的地球上,第二天的环境可能都比现在的火星更适宜生命生存。而且这还没算上在往返地球和火星途中所受到的辐射。
没有 B 计划:这颗地球就是我们所拥有的一切。
William Bjornson
First of all, a 'base' on the Moon is totally impractical just for the 'reconditioning' that would be necessary to bring the workers back from 1/6th G to Earth's Gravity. It will be necessary to build a "2001" style space station in orbit around Luna to house the workers who will 'commute' to the surface for 12-24 hour shifts and then back to the 1G station and would require no long term 'repair' before returning to Terra when their contracts end... and, regarding a 'power plant', America has become so technologically backward and our politicians so ignorant that our design would probably be a 'coal-fired' power plant...
首先,仅为了让工人从六分之一重力环境重新适应地球重力所需的"调理",在月球上建立"基地"就完全不切实际。有必要在绕月轨道上建造一个《2001太空漫游》风格的太空站,让工人居住——他们可以"通勤"到月表工作12-24小时轮班,然后返回1G重力空间站,这样在合同期满返回地球前就无需长期"修复"......至于所谓的"发电厂",美国技术已如此倒退,政客又如此无知,我们设计的恐怕会是座"燃煤电厂"......
Ronald Valli
funny on the last part. Yet it would probably be Blue Origin and Space-X doing that part.
文章最后那段写的有意思,不过最后可能实现的只会是蓝色起源(Blue Origin)和 SpaceX。
Fred Lipson
Neither one of those two Countries presently has the economy that can support this effort. Putin has wasted a fortune invading Ukraine and China's economy is in terrible shape. Meanwhile Bezos is getting huge experience with nuclear reactors and a joint venture with SpaceX , those two could get it done. AI and robots are no stranger to either Bezos or Musk. Japan and the EU would make for great allies to Blue Origin and SpaceX. I don't see China building anything before we get it done.
目前这两个国家(中国和俄罗斯)都没有能够支持这项努力的经济实力。普京入侵乌克兰已经浪费了一大笔钱,而中国的经济状况也很糟糕。与此同时,贝索斯在核反应堆方面已经积累了大量经验,并且与 SpaceX 有合资企业,这两家公司或许能够完成这件事。无论是贝索斯还是马斯克,对人工智能和机器人都不陌生。日本和欧盟可能会成为蓝色起源和 SpaceX 的绝佳盟友。我认为中国不可能在我们完成之前建成任何东西。
ray King
believe what you will, they can do it
不你信不信无所谓,反正他们(中国和俄罗斯)能做到。
IseeYou
You know BYD (China) makes a better car than Tesla (USA), right?
你知道比亚迪(中国)造的车比特斯拉(美国)的好,对吧?
Scott .
Why? Even if the Moon was solid gold, it would not be worth the cost of bringing it back here Any and every business must first consider payback and risks. There is NOTHING there that is that important or that valuable that we HAVE to have it.
为什么要建月球基地?即使月球是由金子构成的,把它带回地球的成本也不值当。任何企业都必须首先考虑回报和风险。那里没有什么东西重要到或珍贵到我们非得拥有不可。
Dames Logic
Who is going to maintain and take care of this? Such a foolish idea, doesn’t Russia and China have more pressing matters at the moment like stopping a major war?
谁来维护和照料这个(月球基地和发电厂)呢?这是个愚蠢的想法,俄罗斯和中国现在是真闲的没什么事可做了么?比如阻止一场战争什么的?
walter glass
China and Russia want to survive the nuclear war Christians want so the world ends, and they get to go to heaven.
中国和俄罗斯想的是能在核战争中生存下来,而基督徒们则盼望世界末日到来,这样他们就能上天堂了。
Mikey M
Russia is slowing but surely gaining ground in Ukraine, and China can use the market.
俄罗斯正在缓而稳步地在乌克兰取得进展,而中国可以趁此机会占领市场。
Steven W
Sounds to me like another Space Race is on. The US cannot sit by while the Russians and Chinese move forward with building a base on the Moon. That is unacceptable!
在我看来,另一场太空竞赛已经开始了。美国不能眼睁睁地看着俄罗斯和中国推进月球基地建设的计划。这绝无法接受!
Mikey M
While we have largely ceded the Moon to China by betting on Starship (that was contracted to land on the Moon in the Spring of 2024...not a typo... and return, albeit unmanned), this should work out terribly well for both parties. On the other hand, China may as well steal whatever there is of Russian tech. So, sure.
尽管我们(美国)因押注"星舰"计划(该计划曾预计2024年春季实现无人登月并返回——注意,这里的日期没写错——却至今杳无音信)而几乎将月球主导权拱手让给中国,这对双方倒真是"双赢"。至于中国,我敢肯定,他们也能顺便把俄罗斯那点技术家底“摸”个透。
Grinning Fox
So what's the REAL angle here? Con Russia into putting forth most the capital to bankrupt them further and keep them further latched onto China's teet?
那这里面有什么猫腻嘛??骗俄罗斯投入大部分资金,让俄罗斯进一步破产,然后让他们更依赖中国?
Gina PACHAL
Humans were not built to withstand those environments and would need to evolve to survive.
人类生来就无法承受这样的环境,需要进化才能生存。
Unrivaled Plumbing Techs
No, we have technology for that.
才不是,我们(美国)有技术。
john cannon
Humans were not built to live most places on Earth. But we have a technology to bridge the gap.
人类生来也无法在地球上的大多数地方生存。但我们有技术来弥补这个问题。
Dirk Michael
Man has evolved to withstand women = so anything is posible,
人类已经进化到对女人的耐受性 = 所以一切皆有可能。
A F
Not really. There's long term effects on the body that we havent found a way to really combat.
不全对。身体会受到长期摧残,而我们还没有找到真正好用的应对方法。
S H
I don't believe the two nations have a clue just how hard it's going to be to build and live on the moon. I've read the dust is horrendous. We've actually been there with men in spacesuits, and the dust got onto and into everything and it's very destructive.
我不认为这(中俄)两个国家真了解在月球上建设生活有多难。据我所知,月球上的月尘相当难对付——我们(美国)当年穿着宇航服登月时,那些无孔不入的月尘毁坏了所有设备,其破坏力比想象的还要大。
John Domingo
Changes to the Moon could have catastrophic consequences for life on Earth.
对地球上的生命来说,对月球做出改变很可能会带来灾难性的后果。
Random Moniker
As if it would be appropriate for us to team up with either country on such a project.
好像我们真该与其中任何一国合作这种项目似的。
David Giguere
I guess if Russia and China crash enough men and resources into the moon, they may have enough material to build a power station.
我猜如果俄罗斯和中国在探月上投入足够多的人力和资源,他们或许会有足够的材料来建造一座发电站。
this guy
We will probably be fighting a war for the moon here on Earth soon. Once they start blowing up satellites we will probably never get of the planet again. There will be a never-ending debris field travelling thousands of miles a minute around the Earth.
我们可能很快就会在地球上为月球而战。一旦他们开始炸毁卫星,我们可能再也无法离开这个星球了。届时将会有一个永不笑死的碎片群,以每分钟数千英里的速度环绕地球狂转。
JJones
LOL not if AI takes over, they will terminate humanity like in Terminator.
哈哈,如果人工智能接管一切就不会(有战争)了,因为它们会像《终结者》里那样终结人类。
john cannon
It takes quite a bit of energy to keep satellites in near earth orbits. If the satellites were destroyed, the resulting debris field would fall to earth in short order.
walter glass
Alread is. There are 2,600 non-working satellites and Additionally, there were about 3,200 non-functional satellites in Earth's orbit as of February 2025.
维持卫星在近地轨道运行需要很大的的能量。如果卫星被摧毁,由此产生的碎片群将很快坠落到地球上。—— 沃尔特・格拉斯
已经是这样了。现在有 2600 颗废弃卫星,此外,截至今年2月,地球轨道上约大有 3200 颗无法正常运行的卫星。
Mikey M
No. The debris field expands with the explosion, with much of it being launched beyond the atmosphere required to degrade their orbit on human timescales. It's called the Kessler Effect, and it could be strategically realized by sextive and customized destruction of satellites, generally above LOE. One could even launch satellites designed expressly to create a debris field as an area denial weapon. That debris field would, in turn, fall through the LOE orbits such that they become h very risky to exploit.
不。碎片群会随着爆炸而飞的四散,其中大部分碎片会被抛射到大气层之外,在以人类时间尺度上,这些碎片在轨衰减速度极慢。这被称为凯斯勒效应,通过有选择地、有计划地摧毁近地轨道以上的卫星,从战略上可实现这一效应。甚至有人可以专门发射旨在制造碎片群的卫星,将其作为区域拒止武器。而这些碎片群反过来会穿过近地轨道,使得这些轨道变得极具风险。
user-j5s8mj43m7
WTH would want to work with either of those two nations? China would just spy on us the whole time. While the Russian would just argue on who is correct.
天啊,谁会想和那两个国家一起合作啊?中国只会一直监视我们,而俄罗斯只会争论谁才是对的。
Tim Morris
Given that republicans refuse to properly fund NASA we really don't have any choice but to work with them if we want to be in the game.
鉴于共和党人拒绝为NASA提供资金,如果我们想参与其中,我们真的别无选择,只能与他们合作。
Dames Logic
Ridiculous rhetoric renders anything else sad moot. Please try again w/o the silly pablum.
荒谬的论调让其他讨论都成了徒劳。请过脑子后再说话,别老说这种幼稚的废话。
Tim Morris
you must have conveniently forgot it was your Democrat savior Obama who destroyed NASA and made them private instead of Government and they have never recovered from that. They are no longer the leader in space technology they couldn’t even save their own astronauts, Elon and SpaceX did.
你一定是故意忘了,正是你们民主党的'救世主'奥巴马搞垮了NASA,将其私有化并排除政府机构,而且他们至今未能缓过来。NASA 不再是太空技术的领导者,NASA甚至都无法救回自家的宇航员,最后是埃隆・马斯克和他的太空探索技术公司(SpaceX)做到了。